edible hydrophobic coating
Sunflower oil palm oil coconut oil cocoa butter etc. It is free from waxes and has been designed with optimal hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance to achieve good water vapor resistance and barrier properties.
Gum arabic Mesquite gum Tragacanth gum etc.
. The significant difference is that in edible film solid edible laminate is wrapped around the food products. They are created entirely from food-grade ingredients such as proteins polysaccharides or lipids and are usually 5 nm thick. The coating matrix results in.
Gelatin coatings usually depict good transparency mechanical and barrier properties and can be manufactured via an extrusion or casting process. Gelatin is a hydrophobic protein usually found in wheat which is also a globular protein and also used in some edible coatingsfilms due to its low cost and availability. Texcoat FV Pro is a proprietary triglyceride based edible coating.
Bees wax Carnauba wax Jojoba oil Candelilla wax etc. Encouragingly the concept of fabricating nontoxic roll-off and superhydrophobic coatings with edible materials for readily slicking away residual fooddrink-related liquids was recently proposed and demonstrated by researchers from two universities in the United States Colorado State University and University of Illinois at Chicago Wang et al. In contrast the edible coating forming solution is applied to the food product.
Research on edible superhydrophobic coatings for food packaging material 205 sprayed onto the surface of glass a distance of 50 cm with PP as a binder to improve its robustness. Some of the lipids waxes and resins used for development of edible films and coatings are mentioned below. Nanosystems as Components of Edible Coatings.
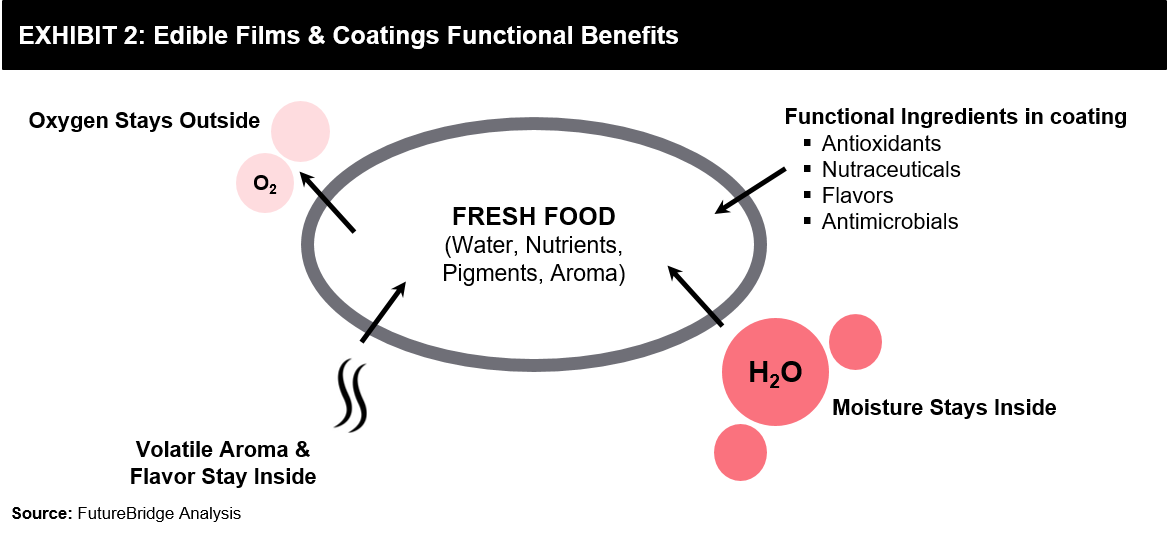
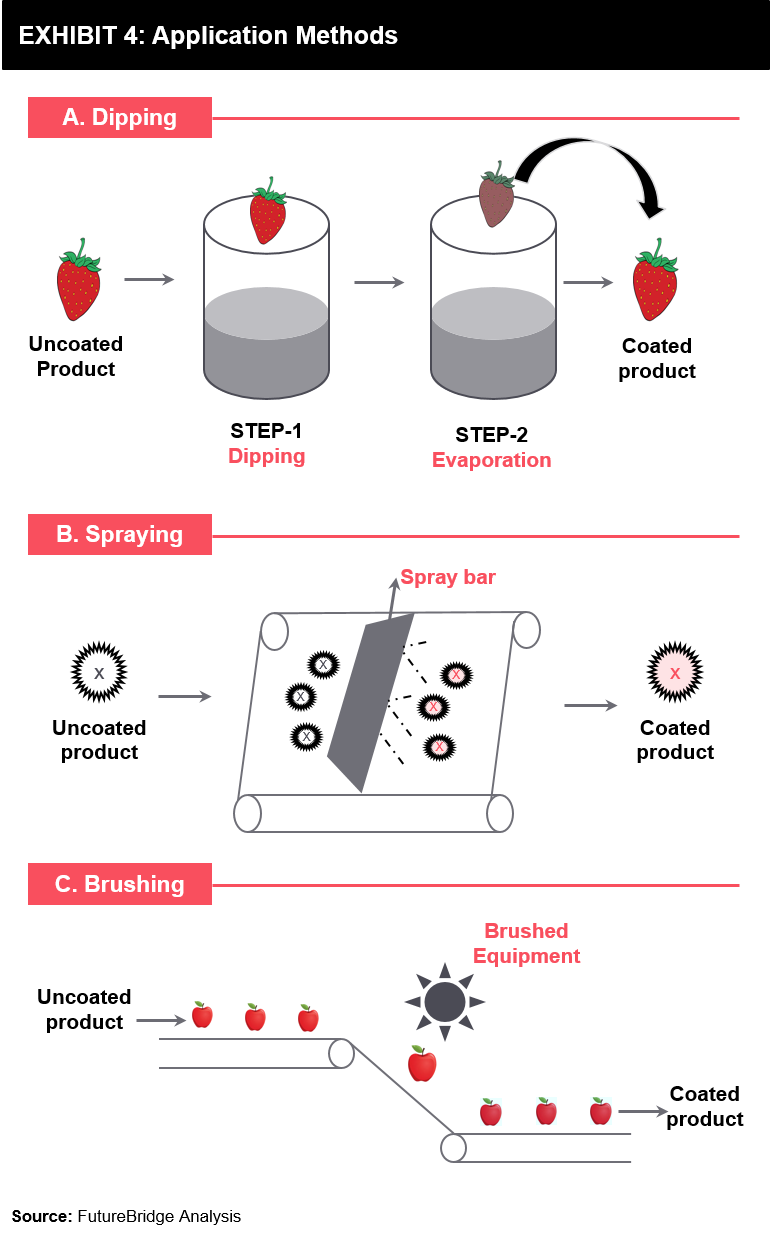
Advances in the preparation of nanosystems that incorporate ingredients acceptable for food products have made it possible to explore the functional modifications of edible coatings that integrate nanoemulsions polymeric nanoparticles nanofibers solid lipid nanoparticles nanostructured lipid carriers nanotubes. 517 Edible Coatings Edible coatings are discussed for meats cheese fruit and vegetables confectionery bakery goods and fast food. Edible films are made by casting and the extrusion process and coating of the edible solution are done by dipping and spraying.
The coated surface was dried at room temperature to realize the superhydrophobic properties.
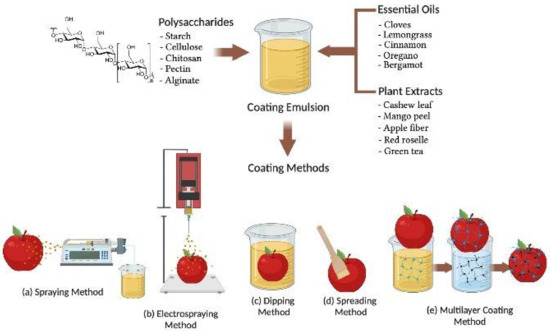
Coatings Free Full Text Polysaccharide Based Active Coatings Incorporated With Bioactive Compounds For Reducing Postharvest Losses Of Fresh Fruits Html

Fabrication Of Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Materials For S
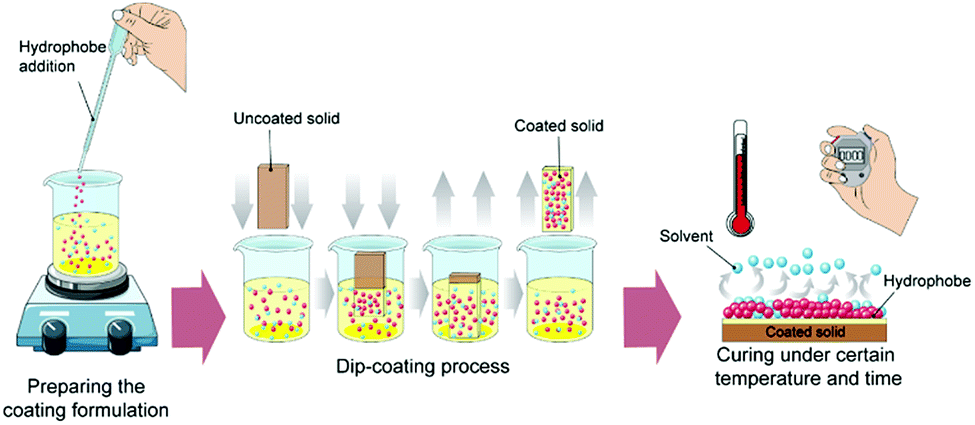
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f

Functional Food Packaging For Reducing Residual Liquid Food Thermo Resistant Edible Super Hydrophobic Coating From Coffee And Beeswax Sciencedirect

Superhydrophobic Coatings With Beeswax And Carnauba Wax Youtube

Pdf Antimicrobial Nanoparticles Incorporated In Edible Coatings And Films For The Preservation Of Fruits And Vegetables Semantic Scholar
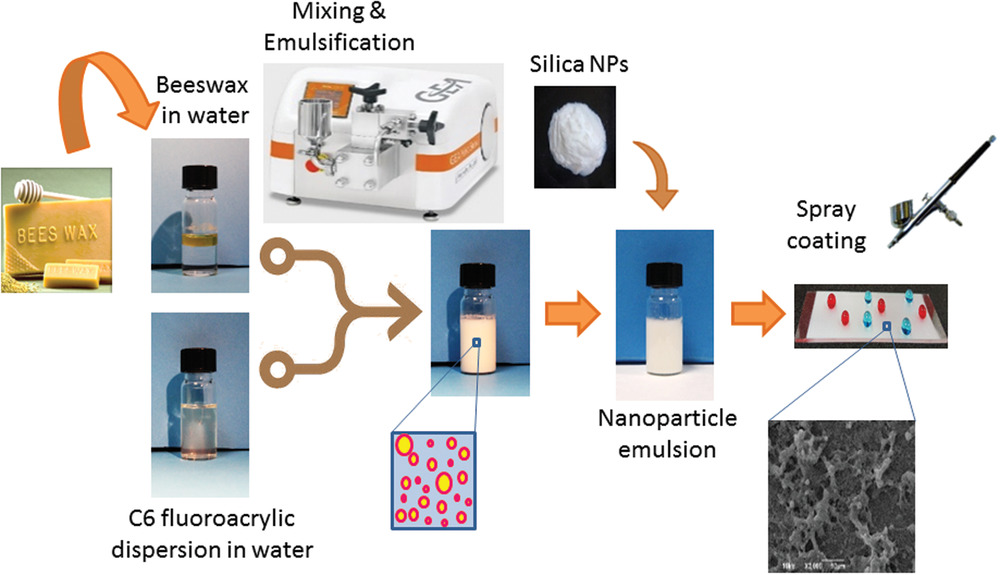
Superhydrophobic Coatings From Beeswax Advanced Science News
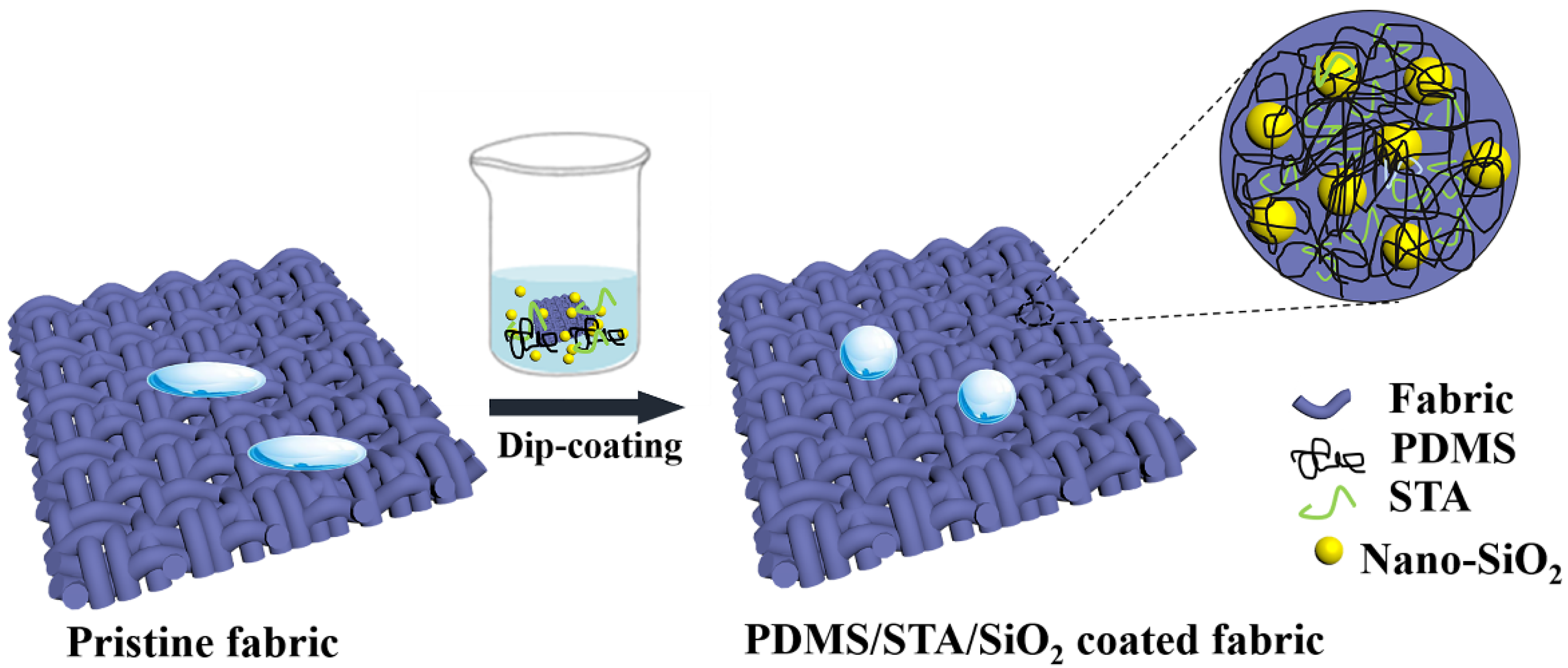
Coatings Free Full Text Dip Coating Approach To Fabricate Durable Pdms Sta Sio2 Superhydrophobic Polyester Fabrics Html
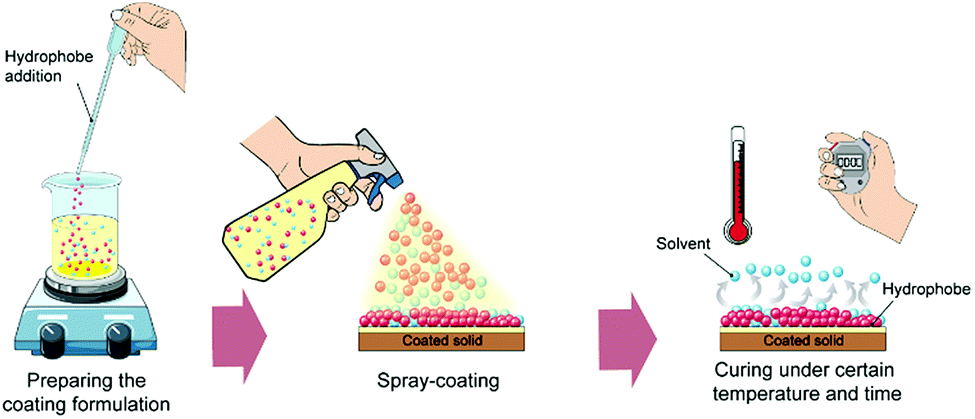
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f

Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Materials Youtube

Edible Coating An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Edible Coating Can Empty Every Last Drop Of Sticky Liquids Like Ketchup Honey Or Syrup
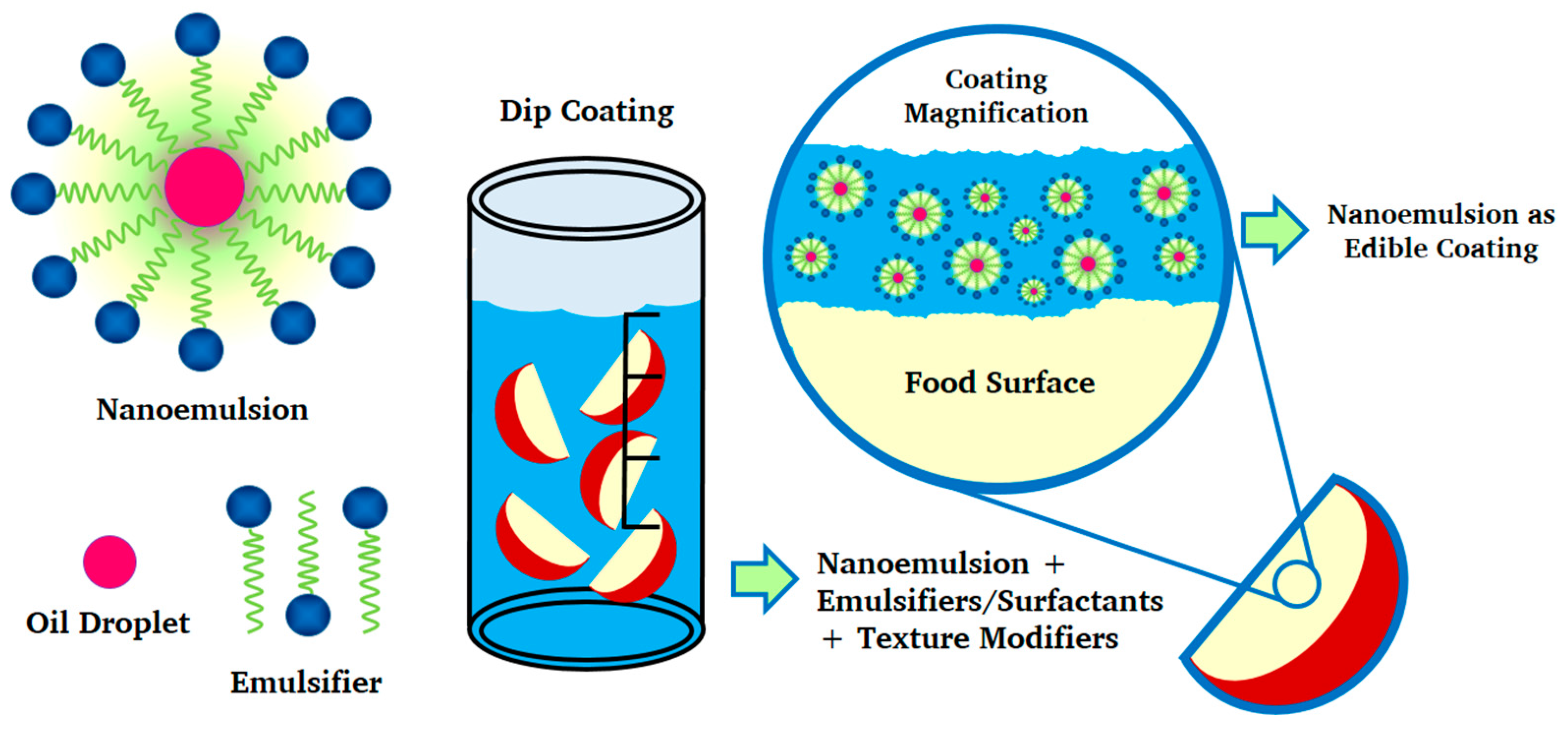
Ijms Free Full Text Nanosystems In Edible Coatings A Novel Strategy For Food Preservation Html
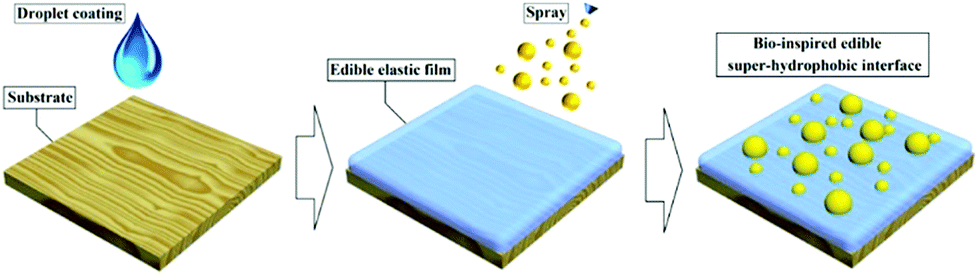
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f

Edible Films Coatings Usage To Prolong Food Stability Technology Times

Comments
Post a Comment